Data integration in the Modern Data Stack
7min • Last updated on Jan 21, 2026

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
According to recent estimates, the global enterprise data management market reached around $108 billion in 2024, and is expected to nearly double by 2030 (Market us).
Data integration plays a key role in this trend. It enables companies to connect their systems and turn raw information into actionable insights.
Key Takeaways:
Data integration refers to the set of processes used to collect, aggregate, and transform data from multiple sources.
It plays a central role in a Modern Data Stack, ensuring that data is unified, reliable, and up to date. It can then be leveraged by analytics and activation tools.
Several integration methods exist, depending on a company’s data volume, frequency, and usage needs.
A variety of specialised tools make integration easier, each with its own advantages depending on the organisation’s complexity, budget, or data maturity.
👉 What exactly is data integration, and how can it be implemented effectively? Discover the methods, challenges and strategic role it plays in a modern data architecture. 🚀
What is Data Integration?
Data integration refers to the process of collecting and bringing together data from multiple sources in order to unify it within a central repository.
This may include both structured and unstructured data, coming from internal systems or external sources. The goal is to centralise and ensure the reliability of this information so that it can be used effectively for analysis or decision-making.
💡 Data integration is sometimes confused with data ingestion. Ingestion refers to the stage of transporting and importing raw data from its source. Integration goes further, as it also involves cleaning, transforming, and standardising the information.
As for data orchestration, this refers to the coordinated management of data flows throughout the entire lifecycle.
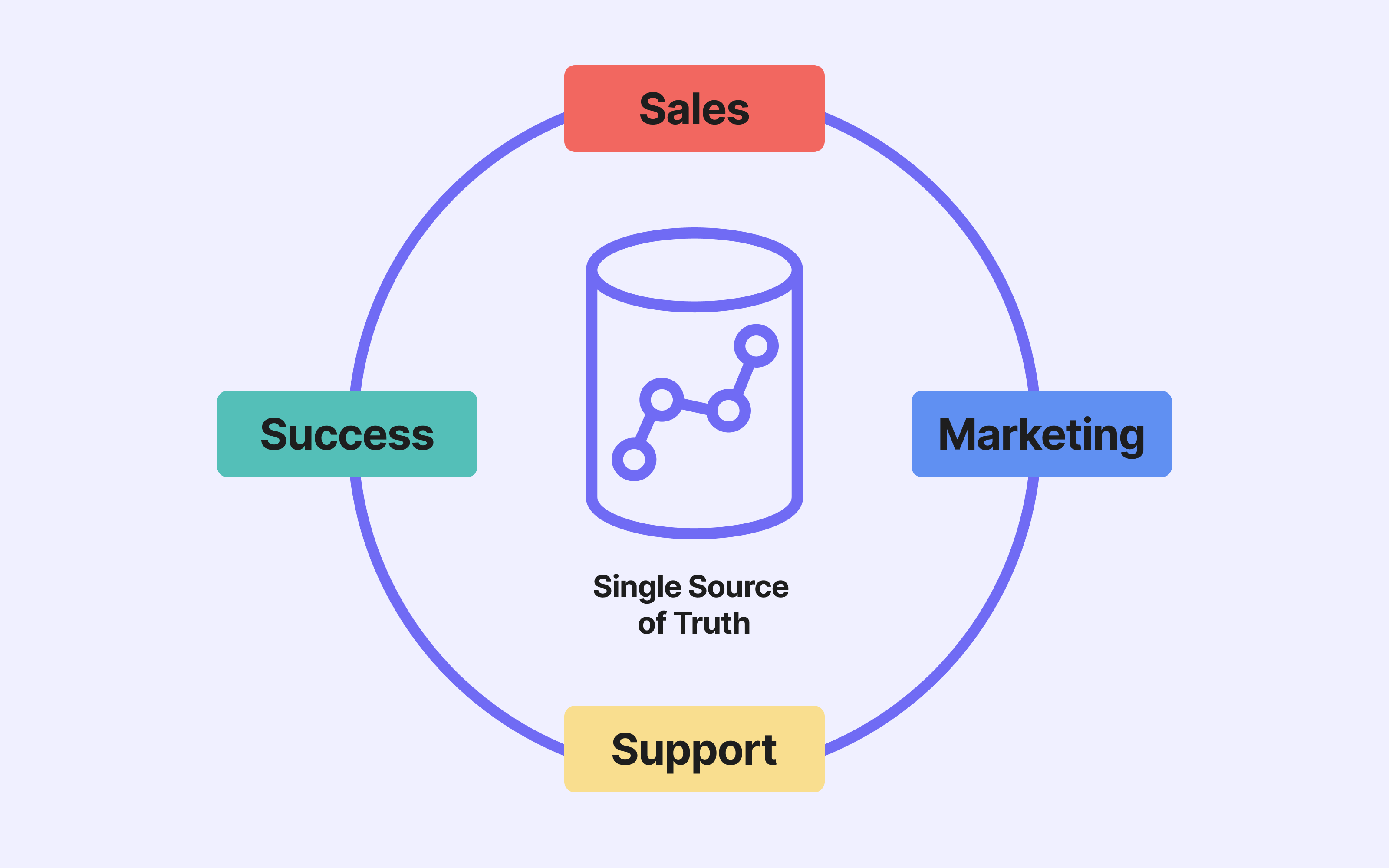
With the rise of Big Data and the widespread adoption of cloud computing, integration plays a key role in building a modern data architecture. It helps create a unified customer view, improve the reliability of reporting, and connect tools across the Modern Data Stack effectively.
Data integration process
Methods and tools
There are several ways to integrate data, depending on the company’s needs, the volume to be processed, or the complexity of the data flows to be connected. All of these approaches aim to reduce or even eliminate manual tasks, which are often a source of errors and wasted time.
ETL vs ELT integration
ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) and ELT (Extract, Load, Transform) techniques are among the most widely used. They allow large volumes of data to be moved between systems through a three-step process.
The difference between the two methods lies in the order of the transformation and loading phases:
In ETL, data is transformed before being loaded into the target warehouse.
In ELT, the computing power of the data lake or cloud data warehouse is used (e.g. Google BigQuery, Snowflake, or Amazon Redshift). Raw data is first loaded, then transformed directly within the warehouse.
ELT is particularly well suited to processing large datasets and to analytical use cases such as dashboards or reporting.
👉 Some of the most well-known ETL/ELT tools include: Fivetran, Airbyte, Rivery, Talend, Informatica, Matillion.
Batch vs streaming
As a general rule, an initial full load is performed, followed by regular updates using batch processing. To improve responsiveness, some companies also adopt continuous ingestion flows.
Change Data Capture (CDC) enables near real-time detection and import of only the data that has changed.
Streaming integration involves processing data in real time as soon as a change occurs at the source. This is especially important for use cases where data freshness is critical: instant personalisation, fraud detection, application monitoring, and more.
Tools like Kafka, Google Dataflow, or Debezium can be used to implement such flows.
The streaming approach is often complementary to ELT. It makes it possible to combine historical data with real-time events in a single repository.
Cloud vs on-premise
The rise of the cloud has transformed data integration methods. Whereas on-premise systems require heavy and rigid configurations, cloud-based solutions offer greater agility, scalability, and interoperability.
Except in highly regulated environments, most integration projects today rely on native cloud services. These solutions provide built-in connectivity with data warehouses such as BigQuery, Snowflake, or Redshift.
This shift reflects the broader trend towards adoption of the Modern Data Stack.
Other approaches
In some cases, companies opt for data virtualisation. This method queries different sources in real time without moving the data, using a single abstraction layer.
Some integrations are built using APIs to connect two tools directly and exchange data in real time. This is a flexible approach, well suited to ad hoc use cases or low-volume data flows.
👇

Modern Data Stack: Best Practices
Benefits and key use cases
Data integration is not just a technical concern. It creates value across the entire organisation by making information more accessible, consistent, and actionable.
It enables systems to be connected, information to be unified, and business tools to be fed with reliable, up-to-date data. Here’s how integration delivers tangible benefits in practice.
1️⃣ Unifying customer data
Customer information is often scattered across multiple tools: CRM, support software, e-commerce mobile app, analytics solution, and more.
Integration makes it possible to centralise this data into a single customer view (SCV), eliminating duplicates and inconsistencies. This allows you to build a 360° Customer View that updates automatically.
This shared foundation is essential for managing customer relationships, personalising messages more effectively, and measuring the value of each user.
2️⃣ Synchronising internal systems
Companies rely on a wide range of applications in parallel: a CRM for sales teams, an ERP for operations, billing or customer support tools, and more.
Without integration, information quickly becomes outdated or contradictory across systems. For example, a customer address updated in the ERP may not be reflected in the CRM.
Data integration ensures consistency across systems. It reduces human error, improves service quality, and saves teams valuable time.
3️⃣ Powering your dashboards
Your teams need reliable data to support analysis and decision-making. That means aggregating information from different sources: sales, marketing, support, finance, etc.
The purpose of integration is to automate this data collection so dashboards are fed continuously. Data is updated in real time, enabling more responsive performance monitoring and a shared view across departments.
4️⃣ Activating data through a composable CDP
Integration also plays a crucial role in the success of marketing campaigns. It supports personalised journeys by delivering the right message, at the right time, through the right channel.
💡 Once centralised in a data warehouse, your data can easily be activated with the composable CDP DinMo. Our no-code Audience Builder and Reverse ETL make it simple to sync audience segments with your advertising platforms, CRM, or Customer Engagement Platform (CEP).
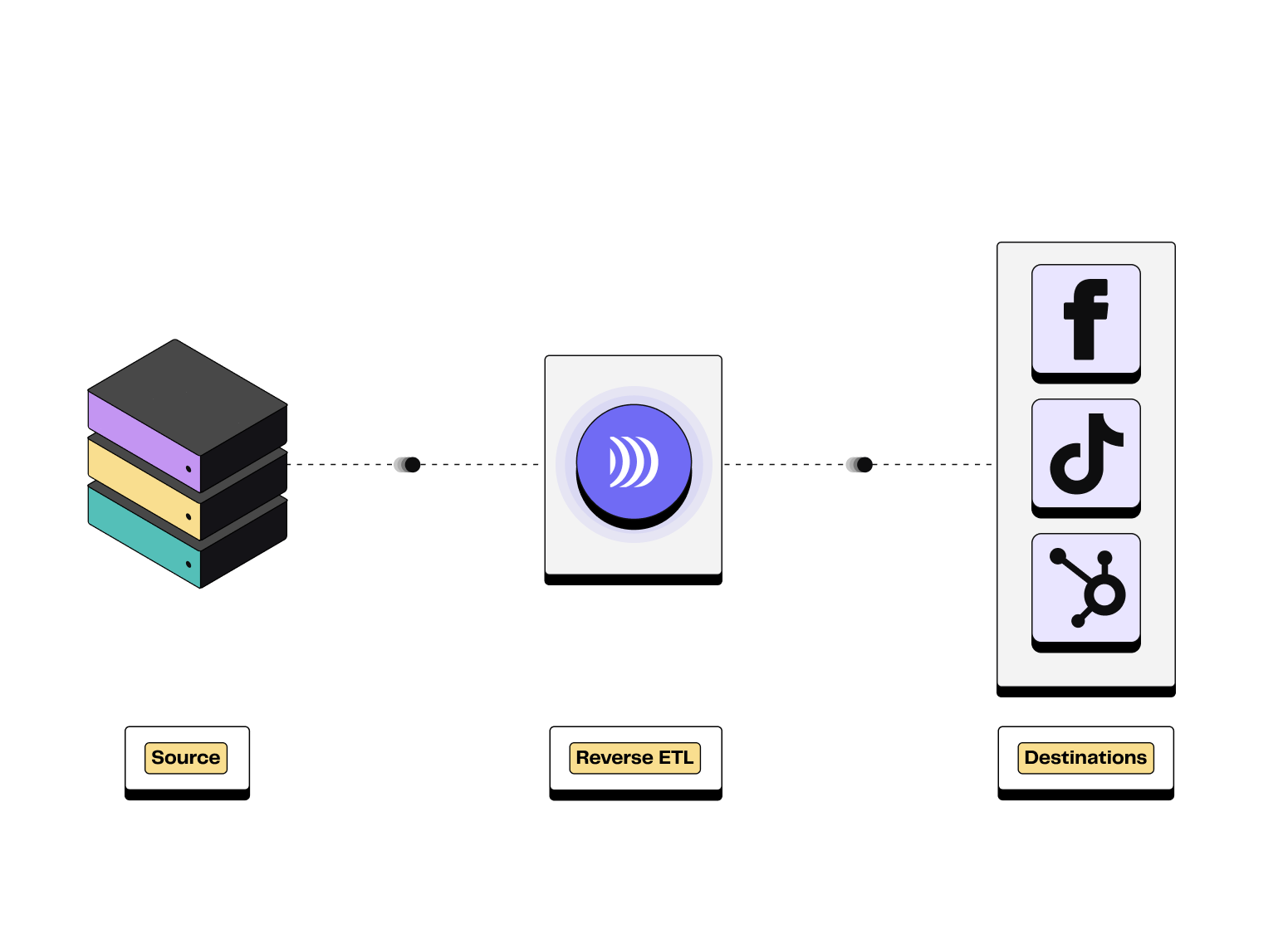
Illustration of Reverse ETL process
This setup ensures personalised campaigns that are always based on reliable, up-to-date data. It is a powerful lever for improving conversion and reducing acquisition costs.
Challenges and best practices for a successful integration project
Key challenges
Before a company can fully capitalise on its data, it must overcome several obstacles:
Multiple and heterogeneous sources:
Data may come from a CRM, ERP, flat files or SaaS tools. This diversity makes connection and standardisation more complex.Poor data quality:
Missing fields, duplicates, and inconsistent formats can compromise the reliability of analysis and lead to flawed decisions.Frequency and volume constraints:
Depending on the required update frequency, business needs, and the volume of data to process, the integration method must be adapted to ensure optimal performance.Growing security and compliance requirements:
Integration must comply with strict rules around personal data protection (GDPR, CCPA), encryption, and access control.Lack of governance:
Without a global view, the proliferation of data flows can lead to technical silos, redundancy, and loss of traceability over data origins.
Our recommendations
A few simple practices can make all the difference when it comes to delivering a successful data integration project.
Map out sources and use cases:
Start by identifying the systems to be connected, the data to be processed, and the teams involved. This step helps prioritise the most critical data flows.Automate your integration pipelines:
Manual processes are prone to errors and inefficiencies. Modern tools allow you to build automated, reliable, and reproducible data flows.Choose tools compatible with your environment:
Make sure your chosen solution includes connectors suited to your business tools, your data warehouse, and your data volume requirements.Establish clear governance:
Define roles and responsibilities for each team, identify the data flows, and document transformations. A strong data governance strategy will ease maintenance and support scalability.Apply security by design principles:
Protect sensitive data, apply the principle of least privilege, and ensure regulatory compliance from the outset.
Data integration and the Modern Data Stack: A new approach
In modern architectures, data integration is no longer just a technical process. It ensures the smooth flow of information between source systems and data warehouses, powering your business tools.
This modular approach involves connecting the components that best suit your needs: transformation and orchestration tools, analytics and visualisation platforms, and activation solutions. Each tool can then work with unified, reliable, and up-to-date data.
This is especially true with the composable CDP DinMo. Flexible and modern, our solution leverages the data already present in your data warehouse to support large-scale activation.
Integration also ties in with other core components of the stack such as orchestration, observability, and business intelligence.
Integration is not an isolated step. It sits at the heart of a broader strategy: building a high-performing, agile, and use-driven data system.
FAQ
How can you integrate data from multiple sources (CRM, ERP, analytics, etc.)?
How can you integrate data from multiple sources (CRM, ERP, analytics, etc.)?
Data integration tools (ETL/ELT, APIs, connectors) are used to centralise and harmonise data from different systems.
These tools extract, transform and load data into a single repository, such as a data warehouse or a packaged CDP, to provide a unified and usable view.
How can you ensure data reliability during integration?
How can you ensure data reliability during integration?
Reliability relies on processes such as validation, deduplication, normalisation, and quality control. It is essential to monitor data flows, document transformations, and set up alerts in case of errors.
Data observability tools also help detect anomalies continuously.
What role does the data warehouse play in a modern architecture when it comes to data integration?
What role does the data warehouse play in a modern architecture when it comes to data integration?
The data warehouse centralises structured and cleaned data from multiple sources, making it easier to analyse. It serves as the foundation for many tools (BI, composable CDP, marketing automation) and enables stronger data governance.
In a modern approach, it becomes the core of the company’s data stack.