How to build a successful Go-To-Market strategy?
8min • Last updated on Sep 22, 2025

Olivier Renard
Content & SEO Manager
[👉 Summarise this article using ChatGPT, Google AI or Perplexity.]
According to CB Insights, the absence of market need is the second leading cause of startup failure (35%), just behind lack of funding (38%). A stark reminder that even established brands are not immune.
Apple Lisa, Amazon Fire, Segway — there’s no shortage of examples of products that failed to find their market. Without a clear launch strategy, even the most innovative offering risks going unnoticed.
Key Takeaways:
A Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy defines how to launch a product, position it, and win over your first customers.
It aligns marketing, sales, and product teams to streamline go-to-market efforts and reduce the risk of failure.
A successful launch is built step by step. Leveraging data and performance analysis helps continuously refine the plan.
A data-driven approach provides better cost control, increases customer loyalty, and improves return on investment (ROI).
🔎 Discover how to build an effective Go-To-Market strategy, its key stages, and its success drivers. How can data, powered by a CDP, accelerate your launch and help secure it? 🚀
What is a Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy?
A Go-To-Market strategy, or GTM, refers to the action plan a company puts in place to launch a product or service on the market.
It defines how to reach the right audience, at the right time, with the right message and the right positioning.
The goal of a GTM is threefold: reduce the risk of failure, accelerate adoption of the new offer, and maximise return on investment.
It’s important to distinguish GTM from a broader marketing strategy. Traditionally, a marketing strategy covers all long-term actions aimed at building a brand.
By contrast, Go-To-Market focuses on a critical moment: bringing a product or service to market.
💡 Although they share the same acronym, this commercial and marketing approach should not be confused with Google Tag Manager, a tag management tool used for tracking.
Why does it matter?
Countless products have vanished simply because they failed to find their audience. These failures are costly: they often involve significant investment and can turn into full-scale industrial flops at launch.
Consumers are exposed to thousands of commercial messages every day. In an era of ad saturation and fierce competition, every product launch needs to be executed with precision.
Today’s customers expect a smooth and personalised experience across their entire journey. This growing expectation increases pressure on profitability and pushes brands to rethink how they bring new offers to market.
A well-designed Go-To-Market strategy helps reduce time to market, lower acquisition costs, and maximise Customer Lifetime Value (CLV). It also strengthens brand perception and creates meaningful differentiation from competitors.
In this context, first-party data is a key asset. It provides reliable customer insights, essential for targeting and executing a GTM plan effectively.
Success stories and famous failures
Iconic successes
iPhone (2007)
The launch of Apple’s now-legendary smartphone remains a textbook example of how to get it right. Steve Jobs managed to present a complex product in simple, compelling terms: an iPod, a phone, and an Internet communicator — all in one device.
It was a meticulously crafted Go-To-Market strategy, combining bold communication, strategic distribution partnerships, and user-centred design. The rest is history: rapid adoption and a revolution in the mobile industry. Today, the iPhone accounts for a quarter of all mobile phones in use worldwide (Statcounter).
Just for the nostalgia: Steve Jobs’ iconic keynote 👇
ChatGPT (2022)
The now-famous chatbot launched by OpenAI at the end of 2022 also experienced spectacular success. Released as a free tool, it reached one million users in just five days.
Its clear, relatable use cases made adoption easy for the general public. Virality on social media and word-of-mouth accelerated its spread even further.
Spectacular failures
New Coke (1985)
The launch of New Coke over 40 years ago remains one of the most widely cited failures in marketing history. In an attempt to counter rival Pepsi, Coca-Cola changed its iconic formula — and severely underestimated the emotional attachment of its customers.
The backlash was immediate, with petitions demanding the return of the original recipe. Just 80 days after New Coke hit the shelves, the Atlanta-based company reversed course.

Which one do you prefer ?
Metaverse (2021)
Meta’s Metaverse has so far failed to truly gain traction. Despite massive investment, the project has struggled due to a lack of product–market fit.
An unclear or overly futuristic positioning, a lack of compelling use cases, and expensive hardware have all slowed its adoption. To date, the Metaverse is estimated to have cost the company led by Mark Zuckerberg over $50 billion.
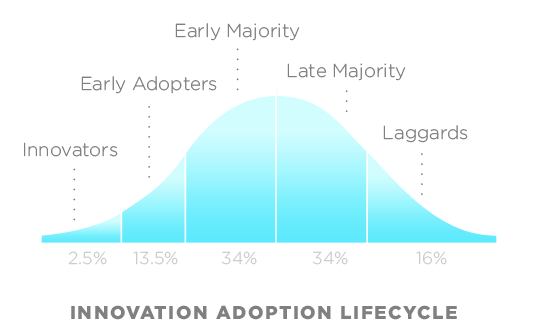
Innovation adoption curve (Source: Wikipedia*)
The stages of a successful Go-To-Market
There is no one-size-fits-all method for a successful launch. Each company must adapt to its market, product, and resources. However, an effective GTM plan follows a clear logic.
1️⃣ Identify your ideal customer profile (ICP) and target market
The first step is to clearly define who your product is for. The ICP acts as a blueprint of the type of organisation that would gain the most value from your solution. Key criteria to consider include industry, company size, and main business challenges.
To go further, personas outline the typical profiles of your potential buyers ? What roles do they hold, what are their needs, and what problems do they face daily?
The success of your strategy hinges on your product or service’s ability to meet one of these needs at the right moment — this is the essence of product–market fit. Achieving this alignment requires in-depth market research, such as using a SWOT matrix.
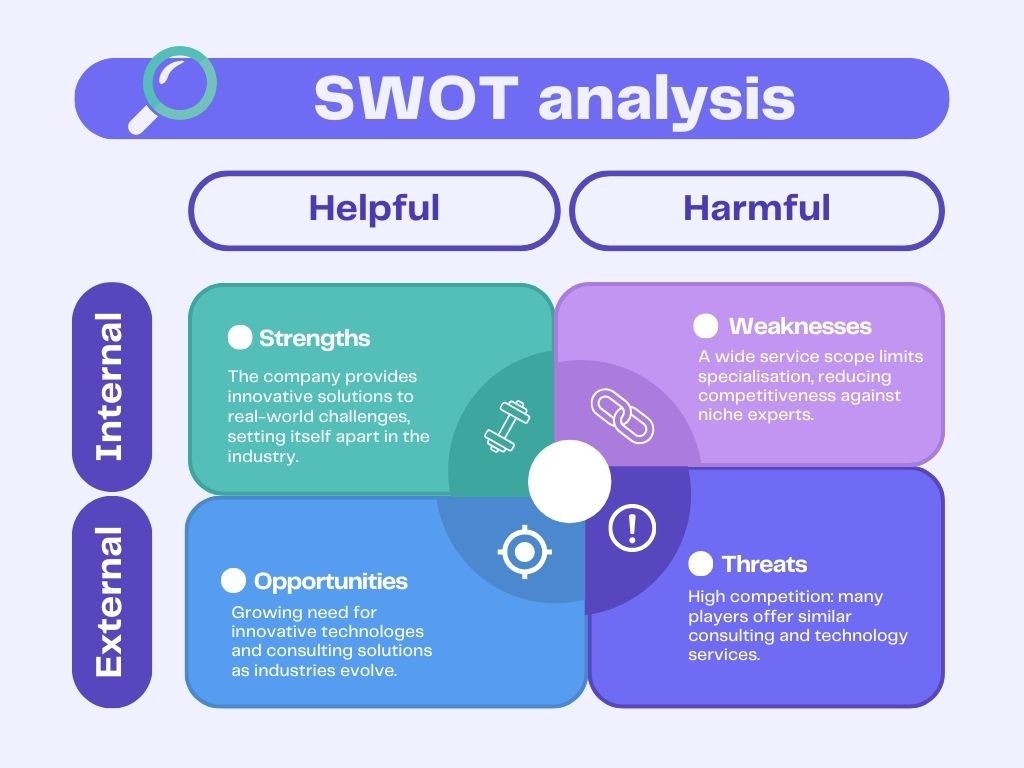
Example of a SWOT analysis
Demographic, behavioural, and transactional data provide invaluable insights to refine this analysis.
2️⃣ Define your value proposition and market positioning
At this stage, there’s only one question to ask: why should the customer choose your product over another? Your value proposition must be clear and truly differentiating.
It rests on your Unique Selling Proposition (USP) — the element that makes you stand out from the competition. This USP fuels your marketing message and guides your communication strategy from the moment you launch.
Introducing an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) — a simplified version of your solution — allows you to quickly test market interest without waiting for a “perfect” offer.
3️⃣ Choose the right channels and distribution strategy
How will customers access your product or service? The choice of channels depends on your target audience and sales model.
Some companies favour a sales-led approach, driven by their sales team. Others go for a product-led growth model, where user experience is the key driver of adoption.
Your visibility and accessibility strategy will also vary depending on your sector:
In B2B :
Traditional outbound channels: prospecting, events, partnerships.
The growing importance of inbound marketing and digital content.
Implementation of Account-Based Marketing (ABM) strategies to target high-value strategic accounts.
Building trust is crucial in longer sales cycles.
In B2C :
Omnichannel strategies: e-commerce, physical retail, digital advertising.
Regular use of social media to drive engagement.
Shorter buying journeys, with higher sensitivity to price and user experience.
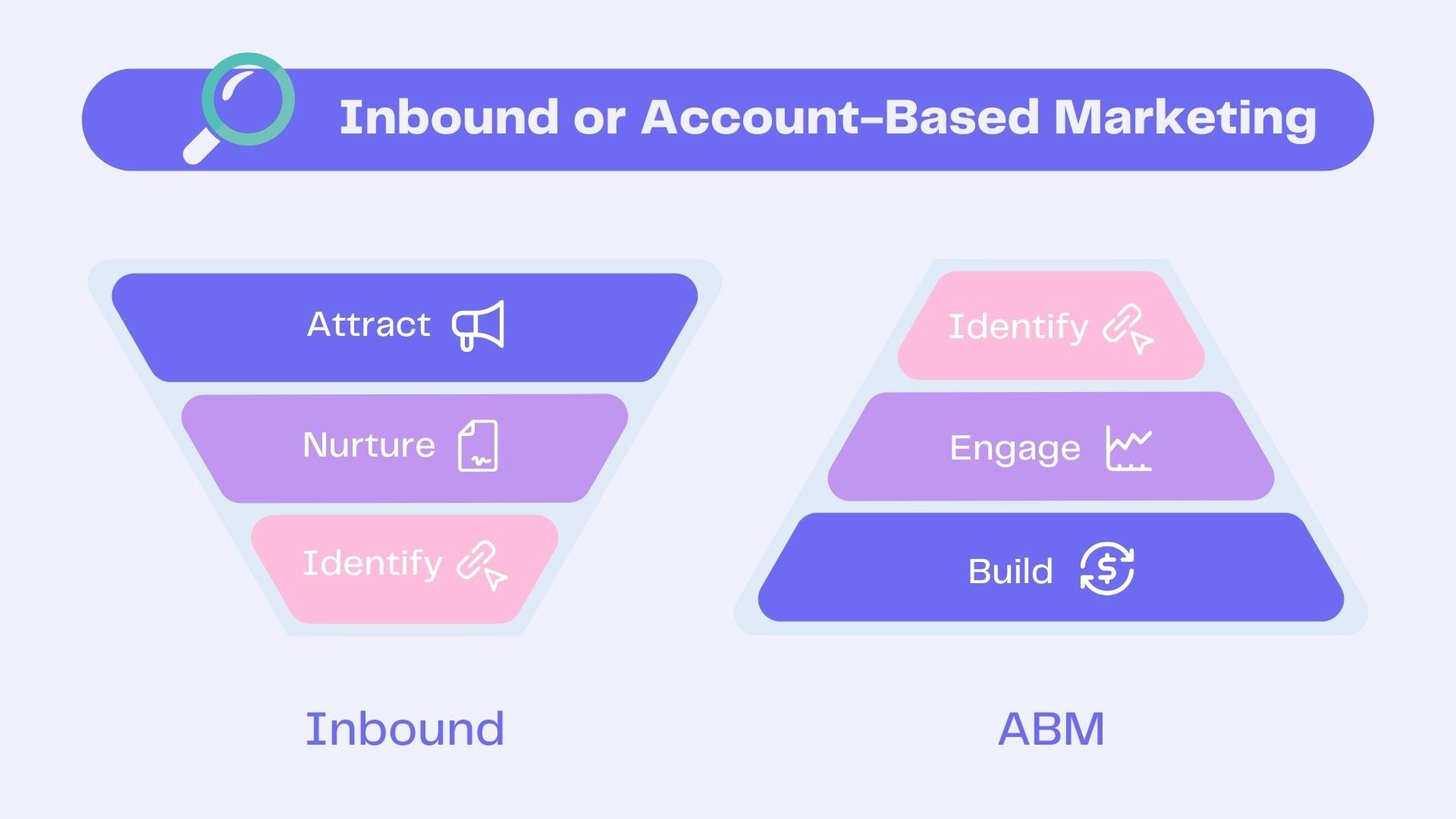
Inbound marketing & ABM
4️⃣ Define your pricing and customer acquisition strategy
Pricing plays a key role in the success of any launch. It must reflect the perceived value to the customer while ensuring a return on investment.
Several pricing models are available: Freemium or subscription-based (common in SaaS), pay-as-you-go or one-off transactions. The best fit depends on your product, market, and customer expectations.
Whether you go for a skimming strategy or a market penetration strategy, your pricing should support acquisition, reflect your brand image, and sustain long-term growth.
5️⃣ Build the action plan and align teams
Execution is a critical stage in any Go-To-Market plan. Its success depends heavily on collaboration between marketing, sales, and product teams.
Alignment around shared goals helps break down silos and improve efficiency. In this setup, data becomes a true performance management tool.
Define the right KPIs to track: acquisition, conversion, satisfaction, churn, LTV. Teams can measure performance, spot friction points, and adjust their plans in real time. Testing, iterating, and involving all stakeholders ensures a continuous improvement mindset.
GTM and data marketing: A new dimension
It’s hard to imagine a Go-To-Market (GTM) strategy based on a rigid, top-down approach with no room for adjustment. This kind of method quickly creates a disconnect between the product and the market’s real expectations.
The use of first-party data and artificial intelligence makes it possible to continuously analyse signals coming from customers. Companies can observe behaviours in real time, identify emerging needs, and adapt their messaging and activation channels accordingly.
This data-driven approach enables teams to fine-tune the GTM strategy post-launch and target each segment with precision. Campaigns become more effective and sales cycles shorter.
The customer experience improves, adoption is faster, and existing clients often turn into true brand ambassadors, actively sharing the value of your offer.
The role of a CDP in a Go-To-Market Strategy
Implementing a data-driven GTM strategy requires a deep understanding of your customers. Unfortunately, data is often scattered across multiple tools.
A Customer Data Platform (CDP) addresses this issue by unifying customer data to provide a usable 360° view accessible to business teams.
With dynamic segmentation capabilities, companies can trigger the right action at the right time, on the most relevant channel. The CDP also simplifies performance tracking, allowing for continuous optimisation of the customer journey.
DinMo’s differentiated approach
DinMo offers a composable, zero-copy CDP that works directly with data stored in your warehouse – no duplication required. Our technology includes Reverse ETL, which enables you to activate customer segments across marketing, sales, and product tools.
DinMo Intelligence enhances this setup with built-in predictive models (e.g. churn, LTV, product recommendation, Next Best Action).
Here are some key GTM use cases:
Retail: Launching a new loyalty programme with personalised communications.
SaaS: Targeting high-value prospects using predictive scoring.
E-commerce: Promoting a new product line with recommendations tailored to each customer.
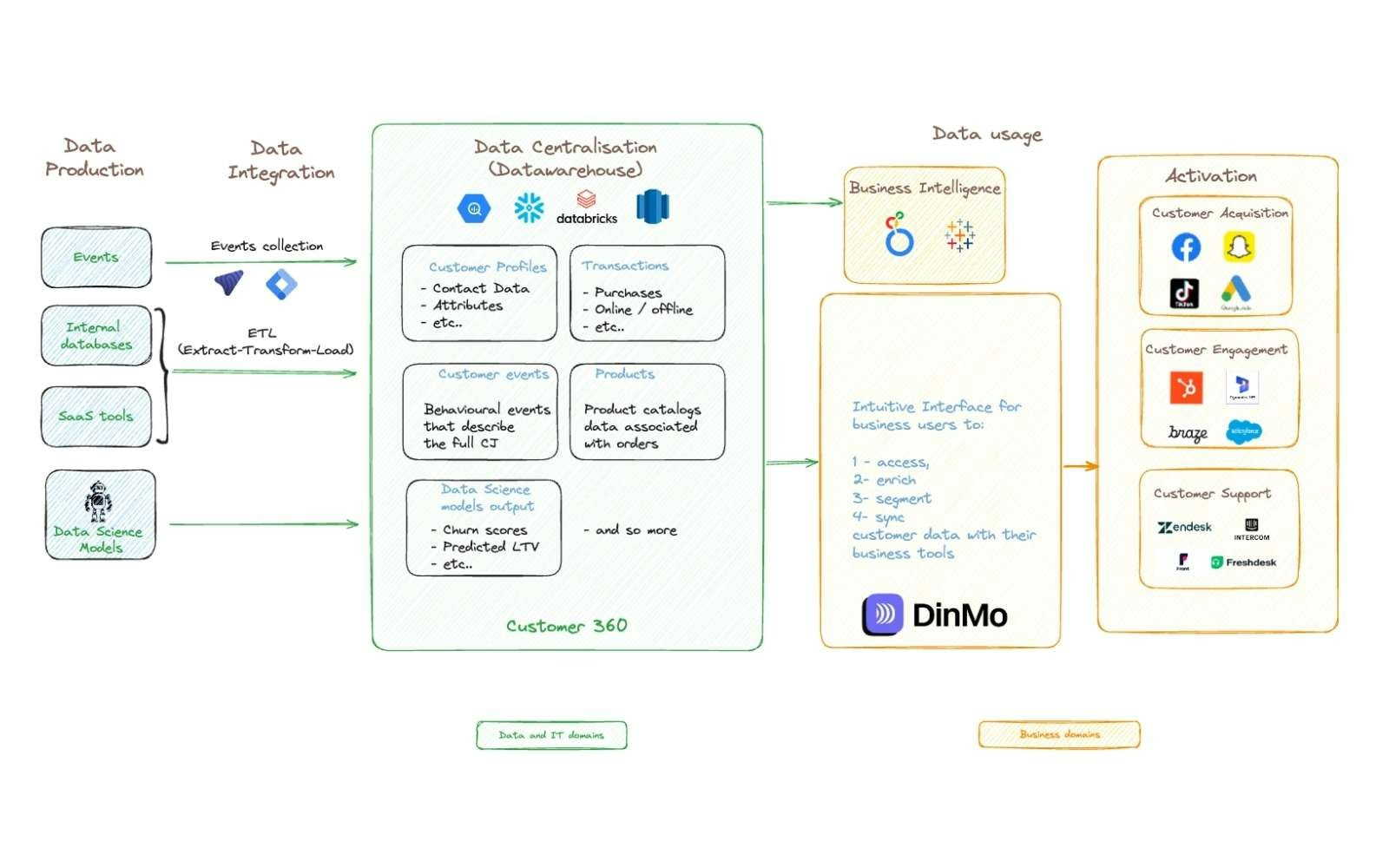
How the DinMo composable CDP works
Conclusion
A Go-To-Market strategy turns an idea into commercial success. It reduces risk during the launch phase, accelerates sales, and maximises return on investment.
A successful launch is not about following a rigid plan. By harnessing the power of data, teams gain autonomy and efficiency.
They orchestrate personalised campaigns, measure impact in real time, and scale their actions effectively. A composable CDP, combined with artificial intelligence capabilities, supports this agile and data-driven approach.
👉 Discover how DinMo helps turn your data into key drivers of success for your upcoming Go-To-Market strategies.
FAQ
How can you measure the effectiveness of a Go-To-Market strategy?
How can you measure the effectiveness of a Go-To-Market strategy?
The success of a GTM plan is measured through key performance indicators such as acquisition rate, customer acquisition cost (CAC), conversions, retention, and Customer Lifetime Value (CLV).
Regularly tracking these KPIs helps identify friction points, adjust the strategy in real time, and optimise the return on investment of all initiatives.
What are the key challenges and best practices for a successful GTM strategy?
What are the key challenges and best practices for a successful GTM strategy?
The main challenges involve data quality, cross-team alignment, and clarity of positioning.
To succeed, you need to start with a well-defined ICP, involve both marketing and sales from the outset, test at a small scale before rolling out, and track precise KPIs.
A data-driven approach helps reduce risk and drive better outcomes.
How do you build a Go-To-Market team?
How do you build a Go-To-Market team?
An effective GTM team brings together marketing, sales, product, and data functions. Everyone should share the same objectives and collaborate closely around common performance indicators.
Marketing drives demand, sales converts it, product aligns features with market expectations, and data provides the insights needed to refine the strategy.
What’s the difference between Go-To-Market (GTM) and Route-To-Market (RTM)?
What’s the difference between Go-To-Market (GTM) and Route-To-Market (RTM)?
The Go-To-Market strategy defines the overall plan for bringing a product to market — from the ICP and pricing to the choice of distribution channels.
Route-To-Market focuses specifically on distribution: how the product reaches the end customer (partner networks, e-commerce, retail, salesforce, etc.).